設計 48V 供電網路時需考慮並攻克的 15 項技術挑戰
為幫助您全面備戰 48V 系統遷移,在開啟您的第一個 48V 設計時,請考慮以下 15 項技術挑戰
The importance of switching frequency quickly becomes apparent to systems designers bringing regulated power to on-board semiconductor devices. With the continual demand for higher performance, CPUs, DSPs and other such devices grow more power-hungry. Accordingly, higher power density regulators with minimal PCB footprints have evolved; these use the latest in IC integration, MOSFETs and packaging. However, even these struggle keep pace with the continuing stream of newer, more powerful devices.
With these pressures, it is tempting to increase regulator frequency, as this reduces the size and board footprint requirements of the associated passive devices – inductors, capacitors and resistors. Conventional thinking, based upon classic hard-switching PWM regulators, is that as frequency increases, then so do switching losses. This is because, in these topologies, regulator MOSFETs incur losses every time they switch, so a higher switching frequency leads directly to higher losses. These inefficiencies are primarily due to high side losses during turn on, Miller gate charge and body diode conduction losses. To make things worse, conventional topologies further magnify the losses as higher input voltages are converted or regulated. These losses introduce a practical limit for the switching frequency of conventional converters and regulators. There is, however, a solution: devices that use the zero-voltage switching (ZVS) topology do not suffer from losses in the same way as conventional designs, allowing them to operate at higher frequencies, which in turn improves performance and dramatically reduces the size of external filter components. Converters and regulators using ZVS also reduce the additional losses associated with large step-down ratios in PWM topologies.
Unlike conventional regulators that rely on hard switching topology, ZVS uses soft switching; this accounts for its improved efficiency and higher density performance. For example, the PI33xx series operates up to 1.5MHz and beyond, which is typically 2x to 3x that of conventional high density regulators. Higher frequency operation not only reduces the size of passive components but also reduces the burden on external filtering components and allows for fast dynamic response to line and load transients.
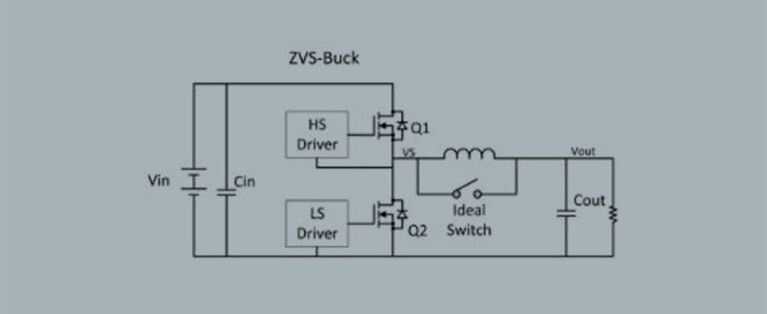
Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram for the ZVS buck technology. Schematically, it is identical to the conventional buck regulators except for an added clamp switch that connects across the output inductor. This switch is added to allow energy stored in this inductor to be used for zero-voltage switching.
Figure 1: ZVS buck technology
Using ZVS addresses the high turn-on losses of the conventional regulator by eliminating high current body diode conduction prior to turn on of the high side MOSFET, bringing the D-S voltage of this MOSFET to zero or nearly zero and producing no high current spikes or damaging ringing. The ZVS action applied to Q1 removes the Miller effect at turn on of Q1, allowing the use of a smaller driver and lower gate drive at turn on.
Regulation from a higher voltage, at a higher efficiency, and in a smaller form factor is realisable with implementation of an improved switching topology. By utilizing the ZVS topology within the Vicor PI33xx, the company has developed a buck regulator that offers high performance regulation up to 36VIN, exceeding the performance found in conventional hard switching, high density regulators. Its high switching frequency allows the external output inductor to be very small, with a total solution size of 25 x 21.5mm; yet it produces up to 120W of output power with a peak efficiency of 98%. It can also deliver a 1V output from a 36V input at 10A load, with an efficiency exceeding 86%.
The same underlying ZVS technology delivers high performance in many other Vicor products, including our AC-DC and DC-DC converters, PRM buck-boost regulators, and the VTM current multipliers.